ESG Strategy Framework
ESG Management System and Vision
ESG Management System
Mission and Vision
SK Gas is committed to practicing ESG management aligned with its corporate mission and vision and leading the way in responding to climate change by pursuing a major transition to a Zero Carbon business portfolio. To this end, SK Gas has established the ESG vision of ‘Sustainable Energy, Better Future’ and set key focus areas based on the ESG directions of ‘For the Planet’, ‘With Stakeholders’, and ‘Through Transparency’.
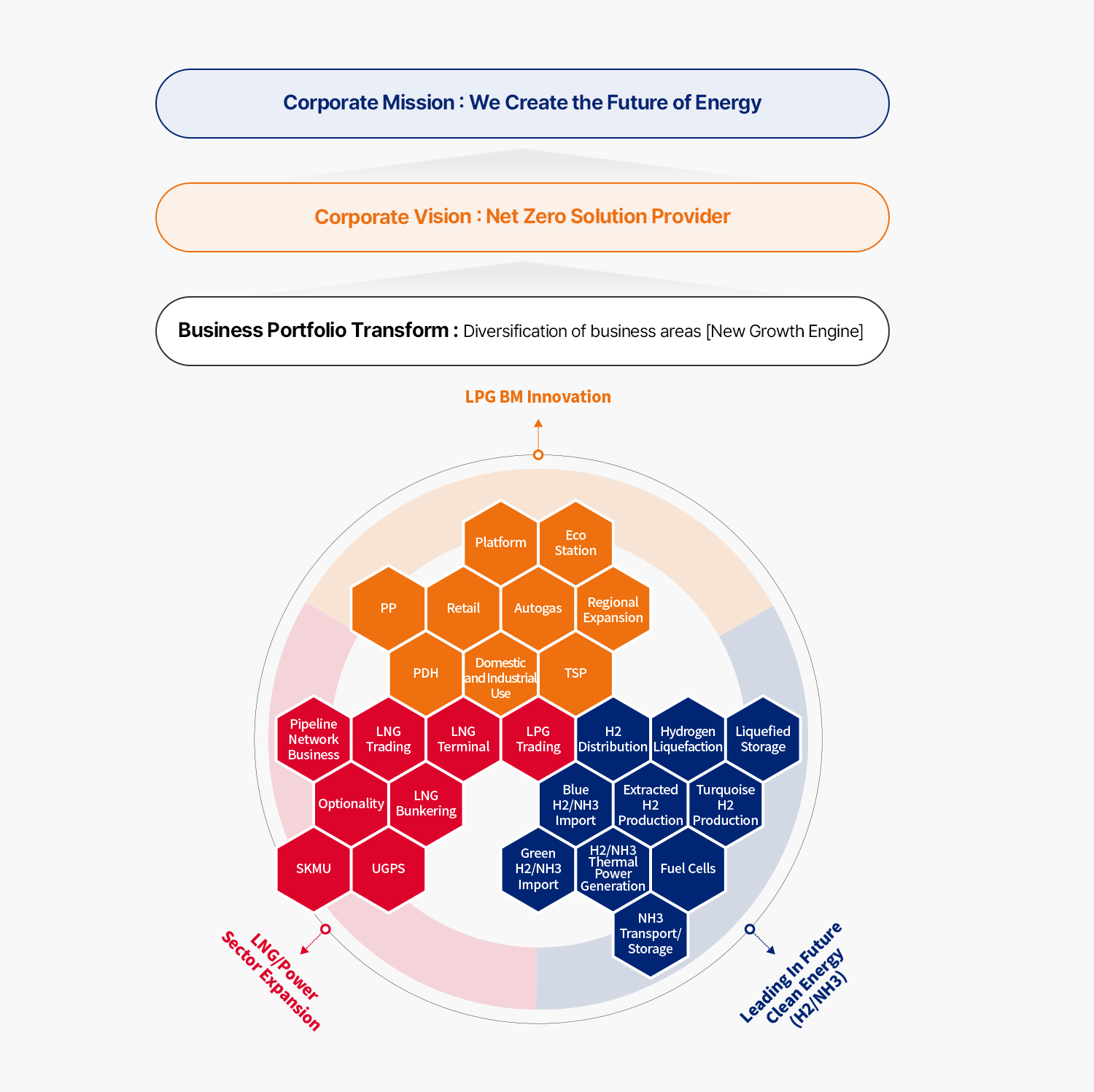
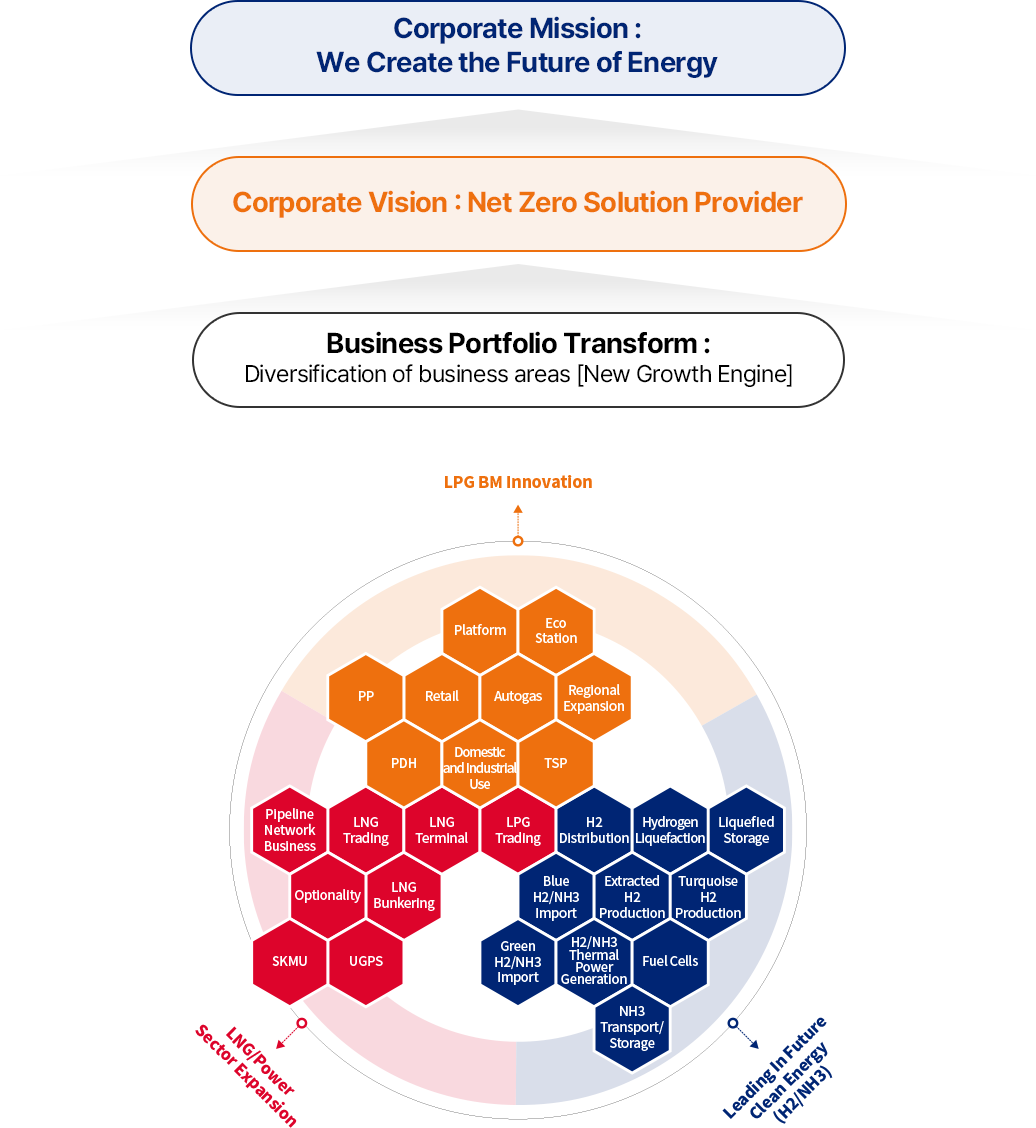
- Corporate MISSION: We Create the Future of Energy
- Corporate MISSION: Net Zero Solution Provider
- Business Portfolio Transformation: Diversification of business areas [New Growth Engine]
- LPG BM Innovation
- Platform
- Eco Station
- PP
- Retail
- Autogas
- Regional Expansion
- PDH
- Home and Commercial Use
- TSP
- LNG/Power Sector Expansion
- Piping Network Business
- LNG Trading
- LNG Terminal
- LPG Trading
- Optionality
- LNG Bunkering
- SKMU
- UGPS
- Future Clean Energy Leadership (H2/NH3)
- H2 Distribution
- Hydrogen Liquefaction
- Liquefied Storage
- Blue H2/NH3 Import
- Extracted H2 Production
- Turquoise H2 Production
- Green H2/NH3 Import
- H2/NH3 Thermal Power Generation
- Fuel Cells
- NH3 Transport/Storage
Governance of ESG management
The ESG Committee is responsible for advising and reviewing the company’s mid-to-long-term climate change response strategies and sustainable growth through ESG management. It oversees the organization’s climate-related response activities. The committee regularly monitors and discusses the status of climate change response and management, and reports the results to the board of directors. Additionally, decisions are made to identify and respond to climate change-related risks faced by SK Gas.
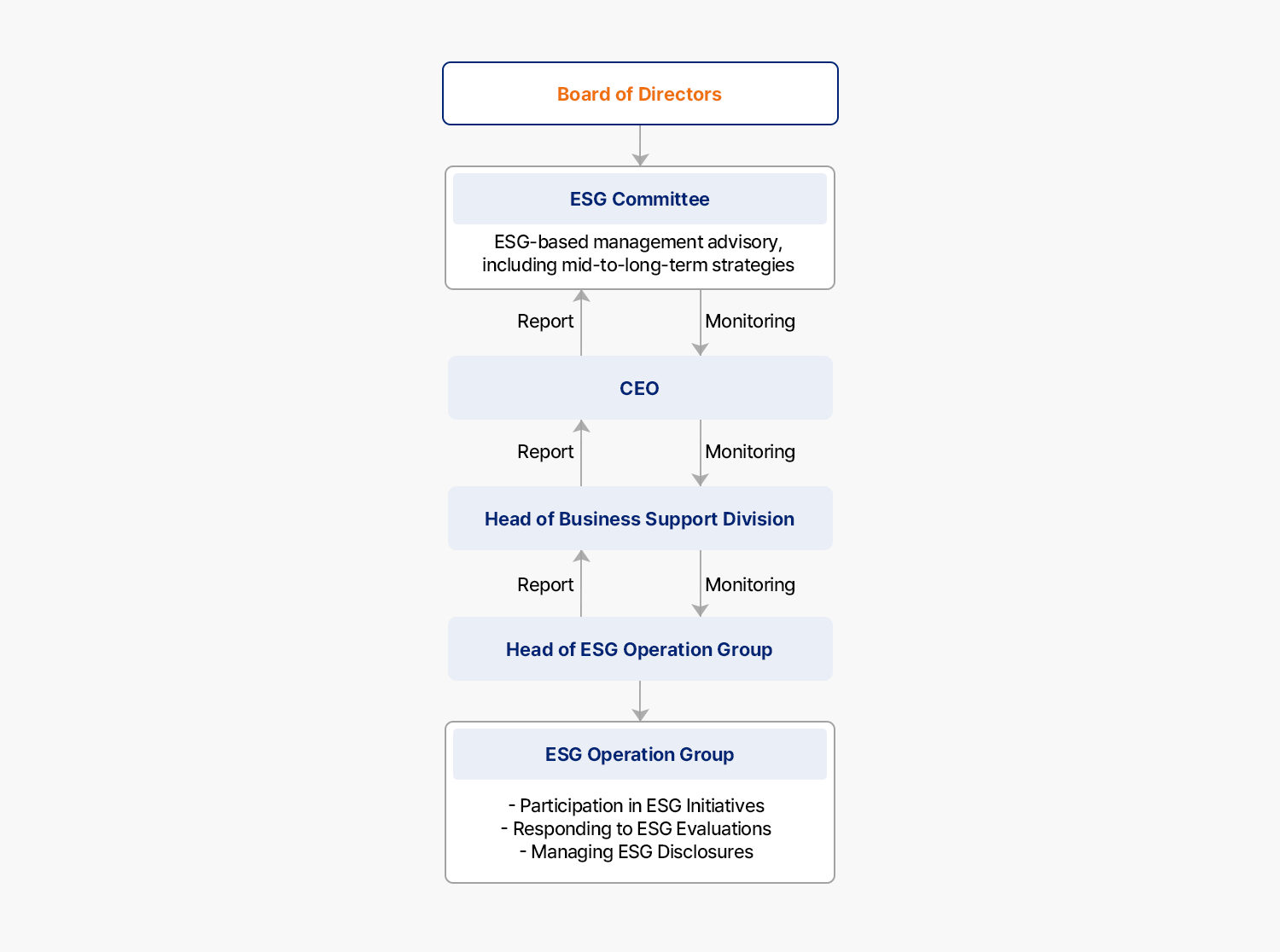
- Board of Directors
- ESG Committee: ESG-based management advisory, including mid-to-long-term strategies
- CEO
- Head of Management Support
- Head of ESG Operations
-
- ESG Operations Group
- Participation in ESG Initiatives
- Responding to ESG Evaluations
- Managing ESG Disclosures
Monitoring by the ESG Operations Group in the Board of Directors
Reports from the ESG Operations Group to the Board of Directors
ESG Masterplan
SK Gas established an ESG master plan in December 2021, recognizing the need for fundamental change to respond to evolving social needs and ensure sustainable growth. The ESG master plan of SK Gas is composed of an innovation plan for transitioning to a Net Zero Solution Provider and strategic directions for each ESG area. Going forward, SK Gas will promote ESG management activities based on the ESG master plan, aiming to secure sustainability for both society and business.
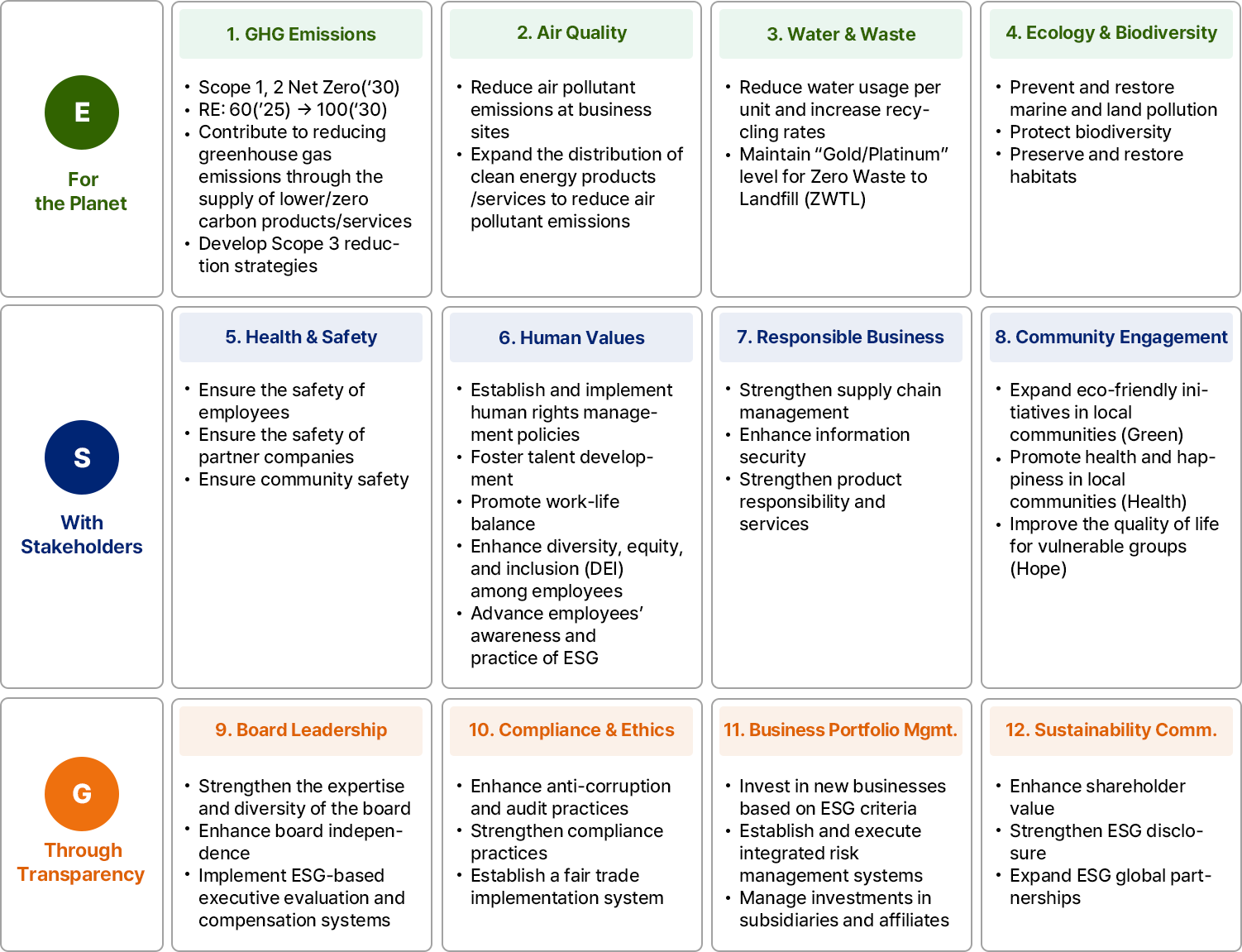
For the Planet
- 1. GHG Emissions (Climate Change Response)
- Scope 1, 2 Net Zero ('30)
- RE: 60 ('25) -> 100 ('30)
- Contribution to GHG emissions reduction through the supply of lower/zero carbon products/services
- Establishment of Scope 3 reduction measures
- 2. Air Quality (Management of Air Pollutants)
- Reduction of air pollutants emissions at business sites
- Expansion of the supply of clean energy products/services to reduce air pollutants emissions
- 3. Water & Waste (Management of Water Pollution and Waste)
- Reduction of water usage Intensity and increase in recycling rates
- Maintenance of ZWTL “Gold/Platinum” level
- 4. Ecology & Biodiversity (Conservation of Biodiversity)
- Prevention and restoration of marine and land pollution
- Protection of biodiversity
- Conservation and restoration of habitats
With Stakeholders
- 5. Health & Safety (Occupational Health and Safety)
- Safety of employees
- Safety of contractors
- Safety of local communities
- 6. Human Values (Employees and Human Rights)
- Establishment and implementation of human rights management policies
- Talent development
- Work-life balance
- Employee diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI)
- Enhancement of employees' ESG awareness/practices
- 7. Responsible Business (Socially Responsible Management)
- Strengthening supply chain management
- Information security
- Enhancing product responsibility and services
- 8. Society Engagement (Community Engagement)
- Expanding eco-friendly initiatives in the community (Green)
- Spreading happiness in the community (Health)
- Improving the quality of life for vulnerable groups (Hope)
Through Transparency
- 9. Board Leadership (Governance)
- Strengthening the expertise/diversity of the Board of Directors
- Enhancing the independence of the Board of Directors
- ESG-based executive evaluation/compensation system
- 10. Compliance & Ethics (Compliance and Ethical Management)
- Anti-corruption/audit
- Strengthening compliance practices
- Establishing a fair trade practice system
- 11. Business Portfolio Management
- Investing in new businesses applying ESG criteria
- Establishing/executing an integrated risk management system
- Managing investments in subsidiaries/affiliates
- 12. Sustainability Communication (Stakeholder Communication)
- Enhancing shareholder value
- Strengthening ESG disclosures
- Expanding ESG global Partnerships
Materiality Assessment
SK Gas conducted a materiality assessment applying the concept of Double Materiality, which considers the financial impacts on the company from an internal perspective and the environmental and social impacts the company has from an external perspective. During the process of evaluating sustainability issues, focus group interviews were conducted with internal and external stakeholders (analysts, ESG experts, etc.) to enhance the reliability of the assessment.
- *The assessment was developed by applying methodologies referenced from GRI (Global Reporting Initiative) 3: Material Topics 2021 and [Draft] EFRAG IG 1: Materiality assessment implementation guidance.
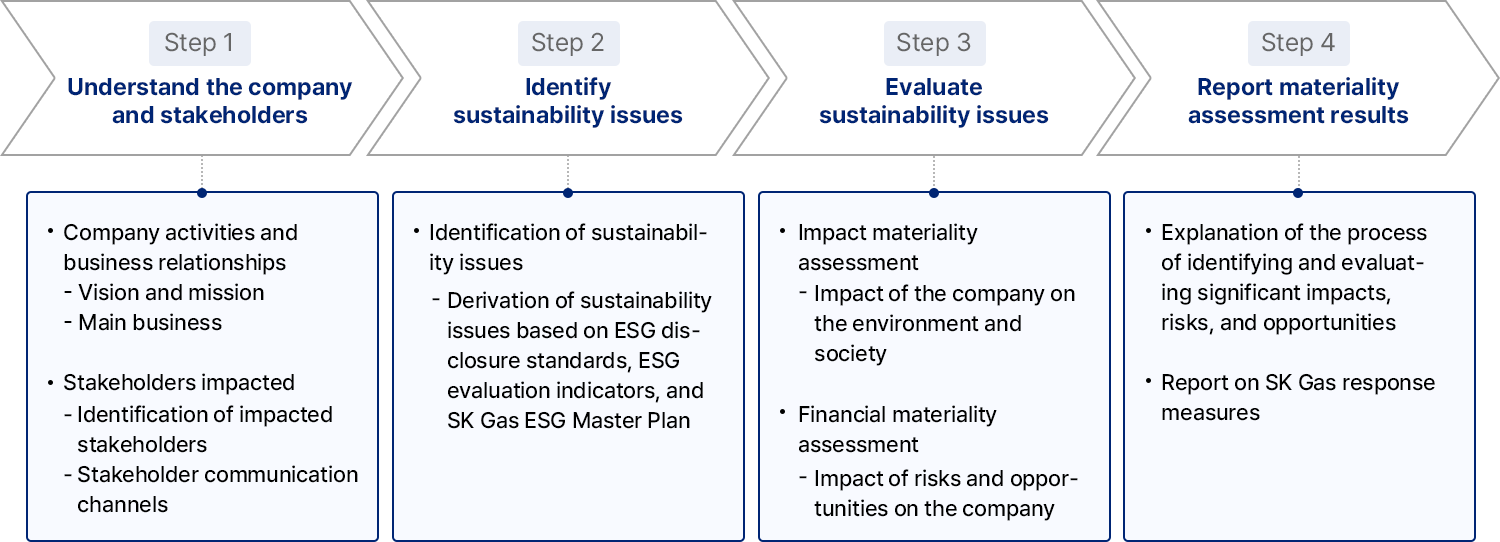
Materiality Assessment Process
-
step1. Understand the company and stakeholders
- Company activities and business relationships
- Vision and mission
- Main business
- Stakeholders impacted
- Identification of impacted stakeholders
- Stakeholder communication channels
-
step2. Identify sustainability issues
- Identification of sustainability issues
- Derivation of sustainability issues based on ESG disclosure standards, ESG evaluation indicators, and SK Gas ESG Master Plan
-
step3. Evaluate sustainability issues
- Impact materiality assessment
- Impact of the company on the environment and society
- Financial materiality assessment
- Impact of risks and opportunities on the company
-
step4. Report materiality assessment results
- Explanation of the process of identifying and evaluating significant impacts, risks, and opportunities
- Report on SK Gas response measures
- 1) ESRS: European Sustainability Reporting Standards.
- 2) Evaluate only in cases of negative impact.
- 3) Evaluate only in cases of potential impact.
Materiality Assessment Matrix
Utilization of Materiality Assessment Results
SK Gas assessed both the impact of its activities on the environment and society, as well as the financial risks and opportunities that external sustainability issues pose to the company. This assessment was based on the results of a double materiality assessment. By integrating response strategies for these identified and evaluated impacts, risks, and opportunities into its corporate strategy, SK Gas is enhancing its corporate sustainability.
ESG Key Indicators
Based on various global ESG guidelines, SK Group provides ESG key indicator guidelines tailored to the industries of its members. Referring to these guidelines, SK Gas aims for the highest global standards among similar companies for each indicator. To achieve this, we designate responsible organizations for key issues, implement improvement measures, and disclose the results annually. Policies and strategies for major issues are communicated with stakeholders through the Sustainability Report and the official website. Additionally, recent three-year performance records and future three-year plans and goals are disclosed through the ESG Data Hub.
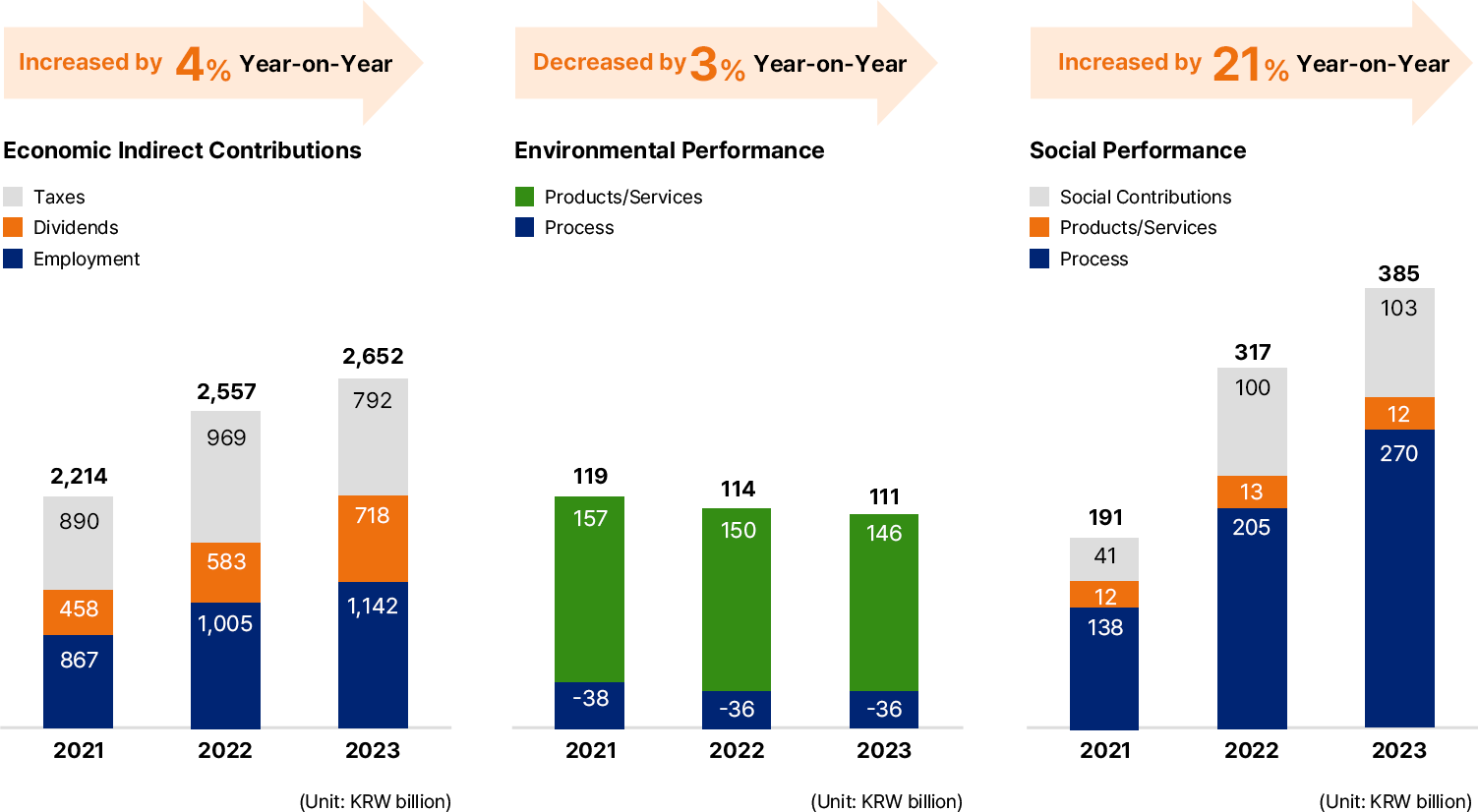
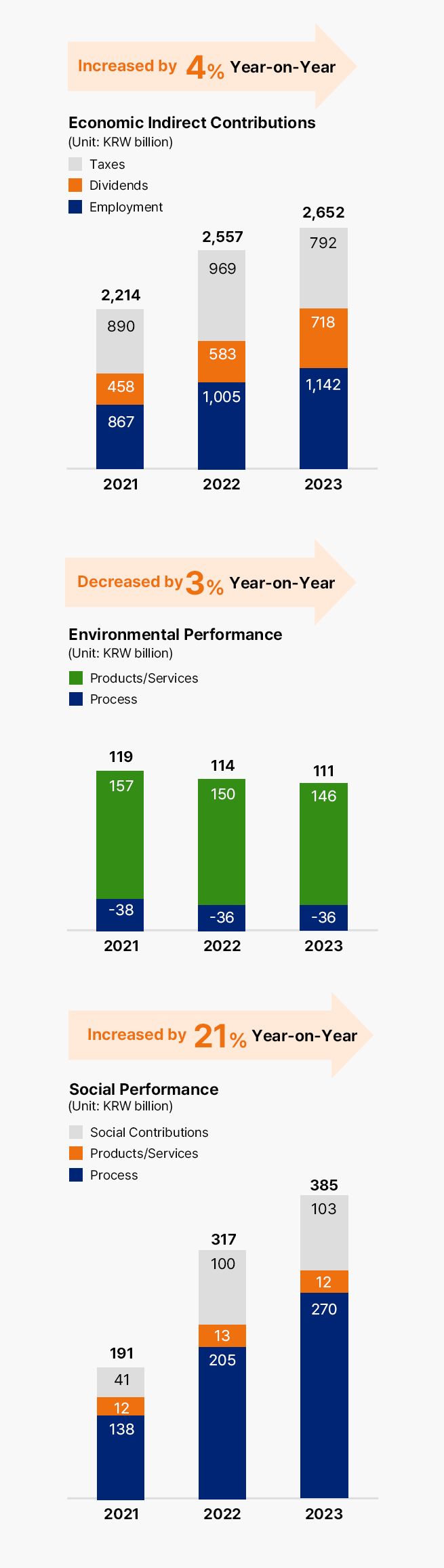
Social Value
DBL Management


SK DOUBLE BOTTOM LINE
- Economic Value: The final outcome of corporate economic activities, disclosed according to generally accepted corporate accounting standards.
- Social Value: The social performance created by generating profits through corporate economic activities and reducing social damage costs.
Pursuing social value based on a human-centered management philosophy rooted in happiness management.
SK aims to achieve sustainable growth by incorporating the Double Bottom Line (DBL) management philosophy, which simultaneously pursues and manages Economic Value (EV) and Social Value (SV), moving beyond the traditional Single Bottom Line that focuses solely on Economic Value and profits.